 |
rotate
1.0
Bit rotator
|
 |
rotate
1.0
Bit rotator
|
#include <HexString.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| HexString (std::string str) | |
| HexString (const char *str) | |
| Construct a new HexString object In order to do this we first need to parse the hex string. If this is not in the correct format, the we need to raise an exception and bail. More... | |
| virtual | ~HexString () |
| Destroy the HexString object. Before we leave we need to zero out all memory that has been used. std::string only guareties that the memory will be reclaimed. Not that it will be whiped. More... | |
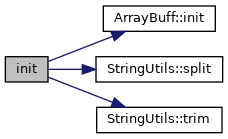
| virtual void | init () |
| The initialisation frunction parses the hex string then creates a vector uint8_t values to create an instance of ArrayBuff. We use new, rather than std::shared_ptr so that we can closely control when it is destroyed, thereby cleaning up the memory used to store values. More... | |
| virtual uint8_t | get_next_byte () |
| Fulfil the interface by calling ArrayBuff to get the next byte. More... | |
| virtual void | write_next_byte (uint8_t byte) |
| Fulfill the interface by calling ArrayBuff to write the next byte. More... | |
| virtual void | write_first_byte (uint8_t byte) |
| Fulfill the interface by calling ArrayBuff tp write the first byte. More... | |
| virtual unsigned int | get_length () |
| Fulfill the interface by calling ArrayBuff to get the length of the buffer. More... | |
| virtual bool | end () |
| Fulfill the interface by calling ArrayBuff to tell if its the end of the buffer. More... | |
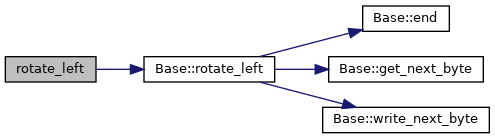
| virtual void | rotate_left () |
| While this looks counter intuative, Base::rotate_left() will call the functions implement in this class, which wil. route the calls to the correct place, in this instance m_arr (the ArrayBuff object) More... | |
| virtual void | rotate_right () |
| Route the call to Base so that calls routed above are called correctly. See comment for previous function. More... | |
| uint8_t | get_rotate_byte () |
| void | reset () |
| std::string | render () |
| Render the rotated result back into a string. More... | |
| ArrayBuff * | get_array_buff () |
 Public Member Functions inherited from Base Public Member Functions inherited from Base | |
| virtual | ~Base () |
Definition at line 25 of file HexString.h.
| HexString | ( | std::string | str | ) |
Definition at line 25 of file HexString.cpp.
| HexString | ( | const char * | hex | ) |
Construct a new HexString object In order to do this we first need to parse the hex string. If this is not in the correct format, the we need to raise an exception and bail.
| hex | Shoud be a string in the format '0xNN','0xNN',...,'0xNN' where NN is a valid hexidecimal numbe. |
Definition at line 18 of file HexString.cpp.
|
virtual |
Destroy the HexString object. Before we leave we need to zero out all memory that has been used. std::string only guareties that the memory will be reclaimed. Not that it will be whiped.
Definition at line 39 of file HexString.cpp.
|
virtual |
Fulfill the interface by calling ArrayBuff to tell if its the end of the buffer.
Implements Base.
Definition at line 122 of file HexString.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 51 of file HexString.h.
|
virtual |
Fulfill the interface by calling ArrayBuff to get the length of the buffer.
Implements Base.
Definition at line 112 of file HexString.cpp.
|
virtual |
Fulfil the interface by calling ArrayBuff to get the next byte.
Implements Base.
Definition at line 84 of file HexString.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 41 of file HexString.h.


|
virtual |
The initialisation frunction parses the hex string then creates a vector uint8_t values to create an instance of ArrayBuff. We use new, rather than std::shared_ptr so that we can closely control when it is destroyed, thereby cleaning up the memory used to store values.
Implements Base.
Definition at line 53 of file HexString.cpp.

| std::string render | ( | ) |
Render the rotated result back into a string.
Definition at line 151 of file HexString.cpp.


|
inline |
Definition at line 45 of file HexString.h.

|
virtual |
While this looks counter intuative, Base::rotate_left() will call the functions implement in this class, which wil. route the calls to the correct place, in this instance m_arr (the ArrayBuff object)
Reimplemented from Base.
Definition at line 132 of file HexString.cpp.
|
virtual |
Route the call to Base so that calls routed above are called correctly. See comment for previous function.
Reimplemented from Base.
Definition at line 141 of file HexString.cpp.
|
virtual |
Fulfill the interface by calling ArrayBuff tp write the first byte.
| byte |
Implements Base.
Definition at line 103 of file HexString.cpp.

|
virtual |
Fulfill the interface by calling ArrayBuff to write the next byte.
| byte |
Implements Base.
Definition at line 94 of file HexString.cpp.
